Delving into the realm of medical procedures, intramuscular injections, often abbreviated as IM injections, stand as a common practice for delivering medications deep into muscles. While this technique offers swift absorption and effectiveness, like a hidden story beneath the surface, it carries its own set of side effects of IM injection. These unintended companions of the treatment journey can vary from mild discomfort to more serious concerns, reminding us that even in medicine, every action has its echo. Let’s embark on a journey to uncover the lesser-known facets of IM injections and their accompanying effects on the canvas of our health.
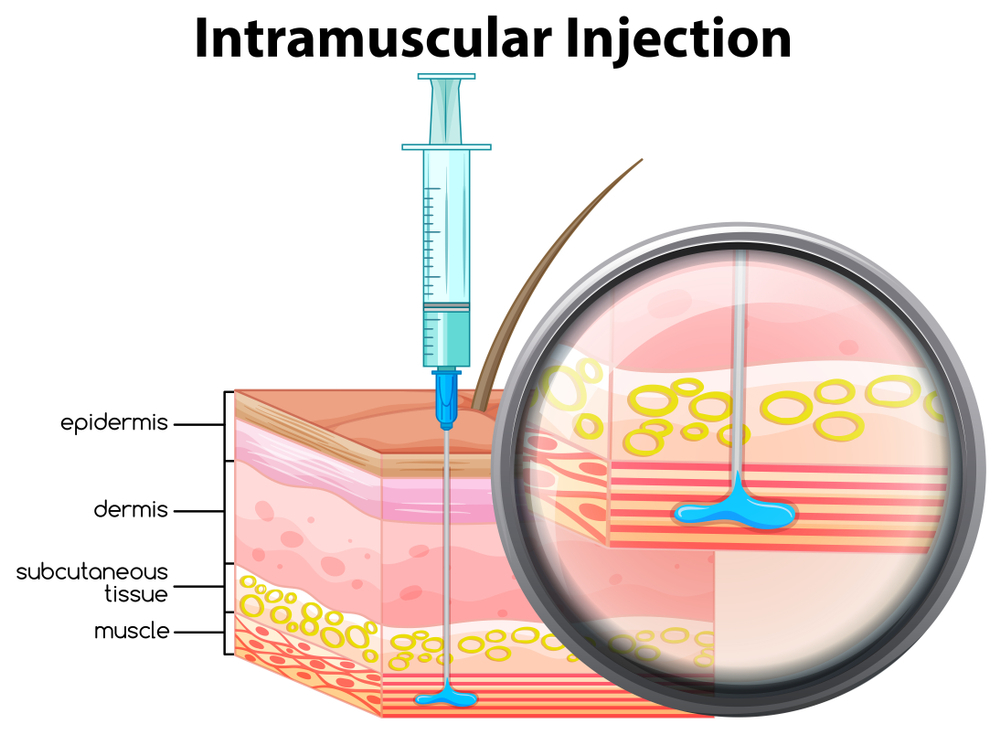
Side Effects of IM Injection
Intramuscular injection, a widely used medical procedure, can have potential side effects. It’s essential to be aware of these reactions for proper care. Let’s explore the common side effects of IM injections:
1. Pain and Discomfort
It’s common to feel a bit of mild pain or discomfort where the injection was given. You can alleviate this by applying a cold compress or taking over-the-counter pain relievers, as your healthcare provider advises.
2. Infection
Getting an infection where the injection is given is unlikely but can happen. Healthcare professionals strictly adhere to hygiene protocols to minimize this risk and ensure sterile conditions during the procedure.
3. Bruising and Bleeding
Bruising or bleeding may occur if a blood vessel is accidentally punctured during the injection. Applying gentle pressure to the area after the injection can help reduce these effects.
4. Allergic Reactions
Severe allergies to the medicine are uncommon but worth noting. Symptoms may include rash, itching, swelling, or difficulty breathing. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to promptly seek medical help.
Remember, intramuscular injections are generally safe and effective. However, if you experience severe or persistent side effects of IM injection, consult your healthcare provider for appropriate guidance.
Uses and Benefits
1. Administration of Medications
Healthcare providers commonly employ intramuscular injection to administer medications, enabling efficient absorption and even distribution throughout the body. This method is particularly beneficial when oral administration is not suitable, as it bypasses the digestive system and ensures direct delivery to the bloodstream.
2. Vaccinations
Intramuscular injections play a vital role in administering vaccines against diseases such as influenza, tetanus, hepatitis, and more. Injecting vaccines into the muscle boosts the immune response, helping the body defend against infections more effectively.
3. Hormone Treatments
Individuals who need hormone replacement therapy often use intramuscular injections to deliver hormones like testosterone or estrogen. This method allows for controlled release of hormones, keeping hormone levels within the optimal range.
4. Antibiotic Administration
Doctors often use intramuscular injections to administer antibiotics. This method ensures rapid absorption and distribution of the medication, allowing for effective treatment of bacterial infections in various parts of the body.
5. Pain Relief
Intramuscular injections can be used to administer pain relievers such as analgesics or anti-inflammatory medications. By targeting specific muscles, these injections provide localized relief, reducing pain and inflammation associated with conditions like arthritis or muscle injuries.
6. Emergency Medications
In critical situations where immediate action is necessary, intramuscular injections are a preferred route for the administration of emergency medications. Drugs such as epinephrine for severe allergic reactions (anaphylaxis) or antipsychotics for acute agitation can be swiftly delivered via this method, ensuring a rapid response.
Benefits of Intramuscular Injection
- Rapid Onset of Action: IM injections help medicines absorb fast, distributing them quickly for faster effects than taking by mouth.
- Controlled Release: By delivering medications directly into the muscle tissue, intramuscular injections provide a controlled release, maintaining therapeutic levels over an extended period.
- Suitable for Non-Oral Administration: Intramuscular injections offer an alternative for patients who cannot take medications orally due to gastrointestinal issues, nausea, or vomiting.
- Higher Bioavailability: Compared to oral medications, intramuscular injections often result in higher bioavailability, meaning a greater proportion of the medication reaches the intended target.
- Improved Compliance: For patients who have difficulty adhering to oral medication regimens, intramuscular injections can ensure better compliance, as they are administered by healthcare professionals.
- Targeted and Localized Effects: By targeting specific muscle groups, intramuscular injections provide localized effects, reducing systemic side effects.
In conclusion, intramuscular injections are a versatile and effective medical technique used for the administration of various medications, vaccines, hormone treatments, and emergency interventions. Their rapid onset of action, controlled release, and targeted effects make them an invaluable tool in healthcare. It’s important to talk to a skilled healthcare provider for advice on using intramuscular injections for your particular situation.
Composition
Intramuscular injections contain specific ingredients that make up the composition of the medication. These ingredients play a crucial role in delivering the desired therapeutic effect. Understanding the composition is essential for both healthcare professionals and patients. Let’s explore the key components found in intramuscular injections.
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API)
The active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is the primary component responsible for the intended therapeutic effect. It is the active substance in the medication that targets the specific condition or symptom being treated. The API can vary depending on the medication, ranging from antibiotics to pain relievers and vaccines. It is important to note that the API concentration may differ among different formulations and brands.
Solvents
Solvents are used to dissolve the API and create a uniform solution for injection. They ensure proper distribution of the medication within the muscle tissue. Two common types of solvents used in intramuscular injections are water-based and oil-based solutions.
- Water-Based Solutions: Water-based solvents, such as sterile water or bacteriostatic water, are commonly used for certain medications. These solutions enable faster absorption and distribution of the medication into the bloodstream.
- Oil-Based Solutions: Oil-based solvents, such as sesame oil or cottonseed oil, are utilized for medications requiring a slow-release effect. These solutions prolong the medication’s action, resulting in a sustained therapeutic effect over a longer period.
Stabilizers and Preservatives
To make intramuscular injections more stable and last longer, stabilizers and preservatives are included in them. They help prevent degradation of the medication and maintain its efficacy. Common stabilizers and preservatives include benzyl alcohol and phenol.
Buffering Agents
Buffering agents are employed to keep the injection solution’s pH balanced. They help ensure that the medication remains in the optimal pH range for stability and effectiveness. Buffering agents can also enhance the patient’s comfort during the injection process.
Other Excipients
In addition to the aforementioned components, intramuscular injections may contain other excipients. Excipients are inactive ingredients that assist in the manufacturing process, stability, or administration of the medication. These can include antioxidants, tonicity-adjusting agents, and antimicrobial agents.
Healthcare professionals need to grasp what’s in intramuscular injections to make safe, effective choices for treatment. Patients can benefit from this knowledge by having a better understanding of the medication they are receiving and any potential allergens or sensitivities they may have.
It is important to note that the specific composition of intramuscular injections can vary depending on the medication, brand, and formulation. Therefore, it is always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or refer to the medication’s package insert for accurate and up-to-date information.
Precautions and Warnings
Administering intramuscular injections requires strict adherence to precautions and warnings to ensure safe and effective treatment. By following these guidelines, healthcare providers can minimize the risk of complications and promote positive patient outcomes.
1. Use Proper Technique for Safe Administration
Administering intramuscular injections necessitates the use of proper technique to minimize the risk of adverse effects. Healthcare professionals should:
- Select the correct needle length and gauge for the injection.
- Ensure proper sterilization of equipment and maintain a sterile environment.
- Accurately determine the appropriate depth for needle insertion.
2. Consider Allergies and Sensitivities
Before administering an intramuscular injection, it is essential to gather information about the patient’s allergies or sensitivities. This knowledge enables healthcare providers to choose suitable medications and avoid potential allergic reactions. Patients should communicate any known allergies or sensitivities to their healthcare provider.
3. Carefully Select Injection Sites
Choosing the right injection site is crucial to avoid complications. Healthcare professionals should follow recommended guidelines when selecting an appropriate muscle for injection, considering factors such as:
- Avoidance of major nerves, blood vessels, and bones.
- Suitability of the muscle for medication absorption and distribution.
4. Observe Hygiene and Sterility Protocols
Maintaining proper hygiene and sterility during intramuscular injections is of utmost importance. Healthcare providers should:
- Thoroughly wash their hands before and after the procedure.
- Cleanse the injection site with an antiseptic solution to minimize the risk of infection.
- Use sterile gloves, needles, and syringes for each injection.
5. Educate Patients on Potential Side Effects
Informing patients about potential side effects is crucial for their understanding and preparedness. Healthcare providers should discuss common side effects associated with intramuscular injections, such as:
- Slight ache or unease where the injection was given.
- Rare occurrences of infection, bruising, or bleeding.
- Allergic reactions, although uncommon.
6. Ensure Proper Dosage Calculation
Accurate dosage calculation is essential to avoid underdosing or overdosing patients. Healthcare providers should consider factors like the patient’s age, weight, medical condition, and the specific medication being administered. Consulting a qualified healthcare professional with expertise and experience is crucial for determining the correct dosage.
By adhering to these precautions and warnings, healthcare providers can safely administer intramuscular injections while minimizing the risk of complications. Strict adherence to proper technique, consideration of allergies, careful site selection, maintenance of hygiene, patient education, and accurate dosage calculation are key to ensuring successful outcomes in intramuscular injection administration.
Dosage Recommendations
1. Importance of Accurate Dosage
Accurate dosage is vital for the success of intramuscular injections. Getting the medication amount right leads to the best treatment results and lowers the chance of bad effects.
2. Individualized Dosage Determination
Dosage for intramuscular injections should be individualized for each patient. Healthcare professionals consider various factors, such as age, weight, medical history, and the specific condition being treated.
5. Trustworthiness in Dosage Administration
Having confidence in healthcare professionals’ trustworthiness reassures patients that they are in safe hands, promoting better treatment adherence and outcomes.
6. Comprehensive Evaluation
Before prescribing an intramuscular injection, healthcare providers conduct a comprehensive evaluation to assess the patient’s condition and select the appropriate medication and dosage.
7. Ongoing Monitoring
After administering the injection, regular monitoring of the patient’s response is essential. Healthcare providers track any changes, ensuring the dosage remains optimal throughout the treatment period.
8. Patient Education
Educating patients about their prescribed medication and the importance of adhering to the recommended dosage fosters responsible self-management and treatment compliance.
9. Individual Sensitivities and Allergies
Healthcare providers must be vigilant about potential sensitivities and allergies to medications. Prior knowledge of these factors helps in choosing the safest dosage for each patient.
10. Collaboration and Communication
Open communication between healthcare providers and patients promotes a collaborative approach to treatment, enhancing dosage adjustments based on patient feedback.
It is crucial to consult with a qualified healthcare provider who possesses the necessary expertise, extensive experience, and a trustworthy reputation to determine the accurate dosage for your specific needs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while IM injections play a crucial role in medical treatments, it’s important to be aware of potential side effects of IM injection. These effects, though generally mild and temporary, can include pain, swelling, and occasionally, minor allergic reactions. By following proper injection techniques and communicating openly with healthcare providers, we can minimize the likelihood of these side effects and ensure a smoother and more comfortable healing process.
*Disclaimer: The information provided in this article on “Side Effects of IM Injection, Uses, Precautions, and Dosage” is for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional regarding any medical concerns or questions you may have.
Author Contribution: Reviewed by Dr. Ram Reddy, MD – General Physician, Dr. Sadiq Mohammed, MD – Orthopedics, and Rajeshwar Rao, Pharm D.
