Welcome to an informative and essential guide on penis diseases—a topic that affects the health and well-being of men everywhere. In this article, we will delve into the various aspects of penis health, exploring both common problems and reliable solutions. Whether you are seeking information to maintain optimal health or require assistance with a specific issue, this comprehensive resource aims to provide you with the expertise, experience, and trustworthiness you need for your health and your life.
Understanding Penis Diseases
The male reproductive system is complex and, like any other part of the body, is susceptible to diseases and conditions. Proper knowledge and awareness play a vital role in identifying potential issues early on and seeking timely solutions. Let’s explore some of the most common penis problems and their respective solutions.

Common Penis Problems and Solutions
The male reproductive system is an intricate network of organs and tissues that play a crucial role in sexual and reproductive health. Unfortunately, like any other part of the body, the penis is susceptible to various diseases and conditions that can significantly impact a man’s physical and emotional well-being. In this section, we will delve into some common penis problems and explore effective solutions to address them. Remember, always consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment.
1. Erectile Dysfunction (ED):
Erectile Dysfunction, commonly referred to as ED, is one of the penis diseases. It is a prevalent condition that affects millions of men worldwide. It is characterized by the consistent inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for satisfactory sexual intercourse. While occasional difficulties with erections are normal, frequent or persistent issues may indicate an underlying problem.
Causes: ED can stem from both physical and psychological factors. Physical causes may include cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, hormonal imbalances, neurological disorders, obesity, and the use of certain medications. On the other hand, psychological factors like stress, anxiety, depression, relationship issues, and performance anxiety can also contribute to ED.
Solutions: The treatment for ED depends on its underlying cause. Consulting a healthcare professional is essential to diagnose the root issue accurately. Some common solutions include:
a. Lifestyle Changes: Adopting a healthier lifestyle can often improve erectile function. Regular exercise, maintaining a balanced diet, quitting smoking, and limiting alcohol consumption can positively impact ED.
b. Medications: Oral medications like sildenafil (Viagra), tadalafil (Cialis), and vardenafil (Levitra) are commonly prescribed to treat ED. These medications work by increasing blood flow to the penis, facilitating erections.
c. Counseling: In cases where psychological factors are contributing to ED, counseling or therapy may be beneficial. It can help address underlying emotional issues and improve overall sexual confidence.
d. Vacuum Erection Devices (VED): VED is a non-invasive device that creates a vacuum around the penis, drawing blood into it to produce an erection. It can be an effective option for some men.
e. Penile Injections or Urethral Suppositories: For those who cannot tolerate oral medications, injections or suppositories containing alprostadil (a vasodilator) can be administered directly into the penis to induce erections.
f. Penile Implants: In severe cases of ED that do not respond to other treatments, surgical insertion of penile implants may be considered. These implants allow men to have an erection whenever desired.
2. Peyronie’s Disease:
Peyronie’s Disease is a connective tissue disorder that results in the development of fibrous plaques or scar tissue inside the penis. These plaques cause the penis to bend or curve during an erection, leading to pain and potentially making sexual intercourse difficult or painful.
Causes: The exact cause of Peyronie’s Disease is not fully understood. However, it is believed to result from microtraumas or injuries to the penis, which trigger an abnormal healing response, leading to the formation of scar tissue.
Solutions: The treatment for Peyronie’s Disease aims to alleviate symptoms and improve sexual function. Common solutions include:
a. Medications: In some cases, oral medications such as pentoxifylline or potassium para-aminobenzoate (Potaba) may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and slow the progression of the disease.
b. Collagenase Injections: An FDA-approved treatment involves injecting collagenase directly into the plaque. Collagenase breaks down collagen, which can help reduce the size of the plaque and improve penile curvature.
c. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT): This non-invasive treatment uses shock waves to break down the plaque and promote natural healing. ESWT has shown promising results in reducing curvature and improving symptoms.
d. Penile Traction Therapy: Traction devices worn on the penis for several hours a day may help stretch the fibrous tissue and reduce curvature over time.
e. Surgery: In severe cases, where other treatments have not been effective, surgical procedures like plication (removing excess tissue) or grafting (adding tissue) may be considered to correct the penile curvature.
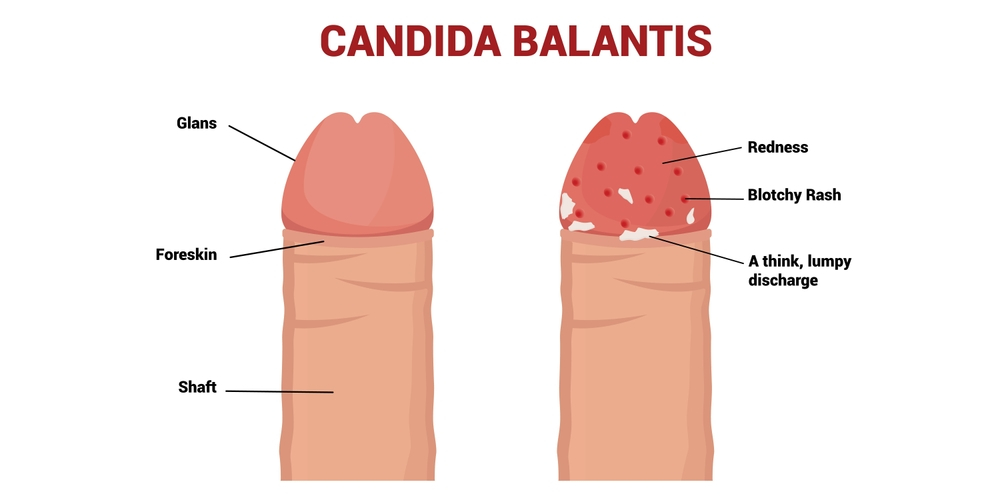
3. Balanitis:
Balanitis refers to the inflammation of the glans (head) of the penis, and it is a common condition affecting males, particularly those who are uncircumcised. It can result from poor hygiene, infections, or skin conditions.
Causes: Balanitis can occur due to several factors, including poor genital hygiene, irritation from harsh soaps or detergents, bacterial or fungal infections, sexually transmitted infections (STIs), or skin conditions like psoriasis or eczema.
Solutions: The treatment for balanitis depends on its underlying cause. Some general solutions include:
a. Good Hygiene Practices: Maintaining proper genital hygiene is crucial in preventing and treating balanitis. Regularly cleaning the area with warm water and mild soap can help reduce irritation and inflammation.
b. Avoiding Irritants: Steer clear of harsh soaps, detergents, or personal care products that can exacerbate balanitis. Opt for gentle, fragrance-free alternatives.
c. Antifungal or Antibiotic Creams: Topical creams or ointments containing antifungal or antibiotic agents may be prescribed to treat balanitis caused by infections.
d. Corticosteroid Creams: In cases of balanitis related to inflammatory skin conditions, topical corticosteroid creams may help reduce inflammation and discomfort.
e. Treating Underlying Conditions: If balanitis is a symptom of an underlying condition, such as psoriasis or an STI, treating the primary cause is essential.
In severe or recurrent cases, a healthcare professional may recommend circumcision as a preventive measure to reduce the risk of future balanitis episodes.
4. Phimosis:
Phimosis is one of the penis diseases. It a condition characterized by the tightness or inability to retract the foreskin over the glans (head) of the penis. While it is normal for the foreskin to be tight in infants and young boys, it should gradually loosen over time. In some cases, however, phimosis can persist into adulthood and cause complications.
Causes: Phimosis can result from various factors, including poor hygiene leading to infections, scarring due to repeated forcible retraction of the foreskin, or underlying conditions like balanitis xerotica obliterans (BXO).
Solutions: The treatment for phimosis depends on its severity and the impact it has on a man’s health and quality of life. Some common solutions include:
a. Gentle Stretching Exercises: Gradual and gentle stretching of the foreskin under the guidance of a healthcare professional may help loosen the tight foreskin over time.
b. Topical Steroid Creams: In mild cases of phimosis, topical steroid creams can aid in softening the skin and reducing inflammation, making foreskin retraction easier.
c. Preputioplasty: This surgical procedure involves making a small incision in the tight foreskin to widen the opening, allowing for easier retraction.
d. Circumcision: In cases where other treatments are ineffective or if phimosis causes significant discomfort or complications, circumcision may be recommended.
It is essential to consult a healthcare professional for a proper evaluation and personalized treatment plan.
5. Priapism:
Priapism is a rare but potentially serious medical condition characterized by prolonged and painful erections that are unrelated to sexual arousal. It requires immediate medical attention as prolonged priapism can lead to permanent damage to penile tissue and erectile dysfunction.
Causes: Priapism can be classified into two types: ischemic (low-flow) priapism and non-ischemic (high-flow) priapism. Ischemic priapism occurs when blood becomes trapped in the penis, causing it to remain erect. Non-ischemic priapism is typically the result of an injury that causes blood to flow into the penis continuously.
Solutions: Prompt treatment of priapism is essential to prevent complications. The solutions depend on the type and duration of priapism:
a. Ischemic Priapism:
- Aspiration: A healthcare professional can drain the trapped blood from the penis using a syringe.
- Medications: Injection of alpha-adrenergic agents can help constrict blood vessels and reduce blood flow to the penis.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to shunt blood flow away from the penis and relieve the priapism.
b. Non-ischemic Priapism:
- Observation: In some cases, non-ischemic priapism may resolve on its own without intervention.
- Embolization: A minimally invasive procedure involves blocking the arteries responsible for the excessive blood flow.

Tips for Maintaining Penis Health
Taking proactive steps towards maintaining good penis health is essential for every man. In this section, we will highlight some practical tips to keep your penis in optimal condition, ensuring a satisfying and healthy life.
1. Hygiene and Cleanliness:
Good hygiene and cleanliness practices are fundamental for preventing infections and promoting penis health. Keeping the genital area clean helps reduce the risk of bacterial and fungal infections, as well as unpleasant odors. Here are some practical tips to maintain proper hygiene:
- Daily Washing: Wash the penis with warm water and mild soap daily. Gently retract the foreskin (if applicable) to clean the entire area thoroughly. Avoid using harsh soaps or aggressive scrubbing, as these can irritate the delicate skin.
- Drying: After washing, pat the penis dry with a soft towel. Ensuring the area is completely dry helps prevent moisture-related issues, such as balanitis.
- Adequate Clothing: Wear loose-fitting, breathable underwear made of natural fabrics like cotton. This allows air circulation, preventing the buildup of excess moisture and bacteria.
- Hygiene After Intercourse: After sexual activity, it’s essential to wash the genital area to remove any bodily fluids or lubricants that may be present.
- Avoiding Douching: Douching the penis is unnecessary and may disrupt the natural balance of bacteria, potentially leading to infections.
By incorporating these hygiene practices into your daily routine, you can significantly reduce the risk of many common penis problems.
2. Safe Sex Practices:
Practicing safe sex is not only crucial for preventing unintended pregnancies but also for protecting against sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Unprotected sexual activity can put you at risk of contracting STIs, which may lead to various complications, including genital warts, chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, and HIV. Here are some safe sex practices to prioritize:
- Condom Use: Always use condoms during sexual intercourse, especially with new or casual partners. Condoms act as a barrier that helps prevent the transmission of STIs.
- Regular STI Testing: If you are sexually active or have multiple partners, consider getting tested regularly for STIs. Early detection allows for timely treatment and reduces the risk of spreading infections to others.
- Communicate with Your Partner: Open communication with your partner about sexual health is essential. Discussing STI testing and any potential concerns can promote trust and ensure both partners are on the same page regarding safe sex practices.
- Limiting Sexual Partners: Reducing the number of sexual partners can also lower the risk of STI transmission. Engaging in monogamous relationships with partners who have been tested for STIs can help maintain sexual health.
- Vaccination: Certain vaccines, such as the HPV vaccine, are available to protect against specific STIs. Consult your healthcare provider to determine which vaccines are appropriate for you.
By making safe sex a priority and being proactive about sexual health, you can significantly lower the risk of encountering complications related to STIs.
3. Regular Check-ups and Screenings:
Regular medical check-ups are essential for monitoring overall health and detecting any potential issues early on. Visiting a healthcare provider for routine check-ups also applies to penis health. A doctor can assess your genital health, discuss any concerns you may have, and provide guidance on maintaining a healthy penis.
During a penis health check-up, the healthcare provider may perform the following:
- Physical Examination: The doctor will visually inspect the penis and surrounding area for any abnormalities, skin conditions, or signs of infection.
- Foreskin Examination: For individuals with a foreskin, the doctor will check for phimosis or any difficulty retracting the foreskin.
- Erectile Function Assessment: If you have concerns about erectile function, the doctor may inquire about your sexual health and may perform additional tests if necessary.
- STI Screening: If you are sexually active, the doctor may recommend STI testing to ensure early detection and prompt treatment.
- Blood Pressure Check: High blood pressure can impact erectile function, so it’s important to monitor it regularly.
- Overall Health Evaluation: The doctor will also inquire about your general health and lifestyle habits, as they can influence penis health.
Remember, regular check-ups not only allow for early detection and intervention but also promote a proactive approach to your overall well-being.
Seeking Professional Help: When to Consult a Doctor
While self-care is essential, there are times when professional medical guidance becomes necessary. We will help you recognize the signs that warrant a doctor’s consultation and guide you on what to expect during a visit.
Conclusion
We hope this comprehensive guide has provided you with valuable insights into penis diseases and their solutions. Remember, being proactive about your health, seeking professional advice when needed, and following a healthy lifestyle will contribute to a fulfilling and satisfying life.
*Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for informational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any medication or treatment. The authors and publishers of this article are not responsible for any adverse effects or consequences resulting from the use of the information provided.
Author Contribution: Reviewed by Dr. Ram Reddy, MD – General Physician, and Rajeshwar Rao, Pharm D.
